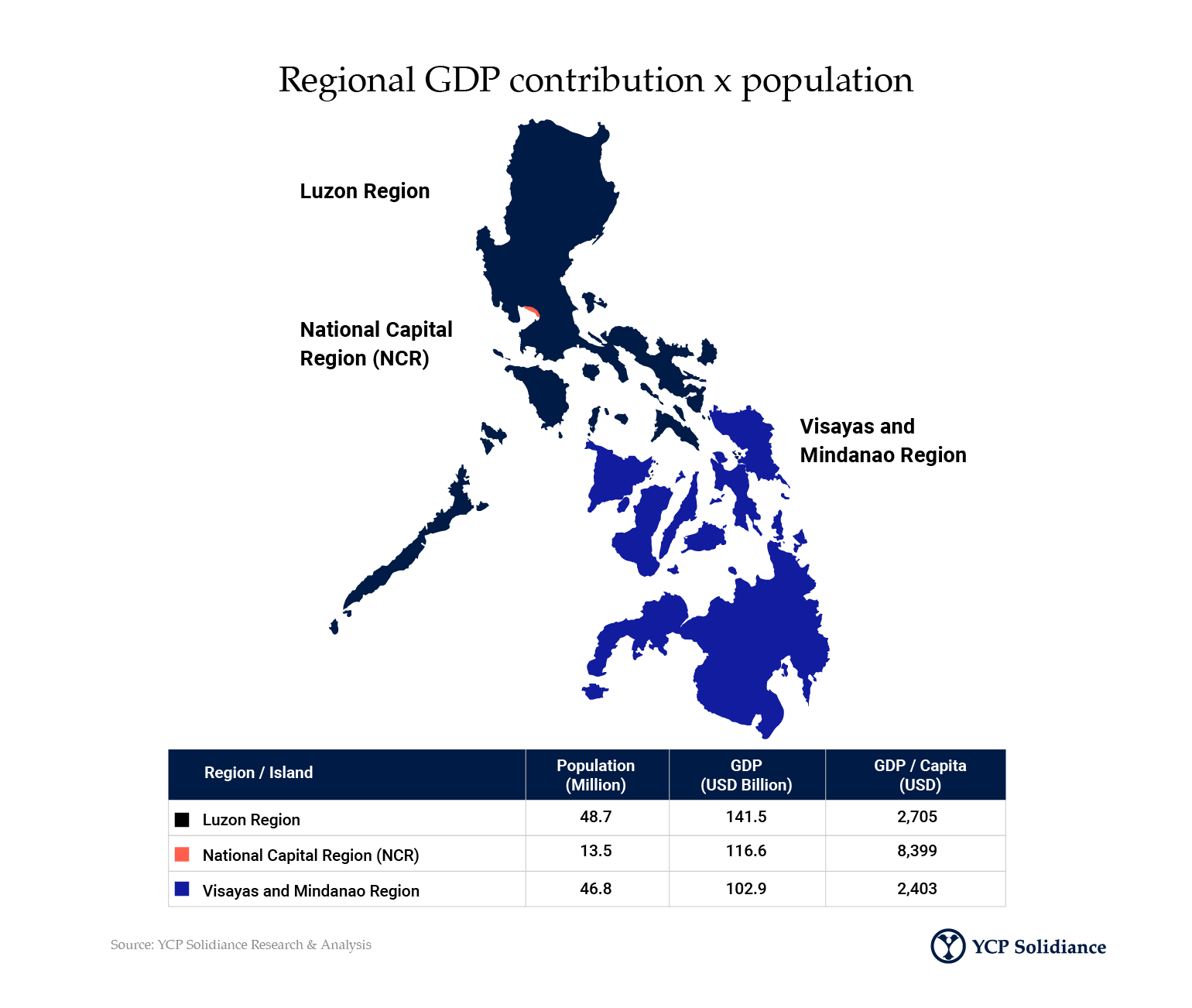
The Philippines’ healthcare industry is a sizable one, driven by both government and out-of-pocket spending at a total value of 18 billion USD in 2020. The country’s National Capital Region, which includes its capital city Manila, contributes the highest amount at 8,399 USD per capita GDP.
The country’s healthcare sector is comprised of four types of care facilities: hospitals, which are further divided between privately-owned and government-run; general clinics and
laboratories, barangay health centers, which focus on vital health services; and rural health units, which are found in provincial areas and provide only the most basic of healthcare
needs.
The onset of the global COVID-19 pandemic and its aftereffects on the Philippine economy have only further emphasized large gaps in the healthcare market, which experts say can be readily
addressed through the adoption of digital technology. Telemedicine is a solution that garnered widespread awareness and acceptance during the pandemic, but healthcare players—and those in
related industries such as medical devices, data services, and even robotics—can find marketable and profitable opportunities in the country’s diverse healthcare space.